Environment Variables
By default, Next.js compiler looks for .env file in projects root folder and reads
its content. In the project files you'll find a file .env.example that contains all the
environment variables that were used in the app environment. The Sample App will not auth with Handcash or load Duro Dogs until you configure the .env file.
Loading Environment Variables
Next.js has built-in support for loading environment variables from .env file into process.env.
An example .env:
ASSETLAYER_URL = "https://api-v2.assetlayer.com/api/v1" ASSETLAYER_APP_SECRET = "<your-assetlayer-app-secret>" HANDCASH_APP_ID = "<your-handcash-app-id>" HANDCASH_APP_SECRET = "<your-handcash-app-secret>" NEXTAUTH_SECRET = "<your-secret>" DOG_COLLECTION_ID = "638665d8506da1c31926beef" ENVIRONMENT="local"
You can also generate a new .env locally which will also generate a random secret by running the following command:
npm run create-env
This loads process.env.ASSETLAYER_URL, process.env.ASSETLAYER_APP_SECRET, process.env.HANDCASH_APP_ID, process.env.HANDCASH_APP_SECRET, and process.env.DOG_COLLECTION_ID into the Node.js environment automatically allowing you to use them in Next.js data fetching methods and API routes. The collectionId for Duro Dogs is "638665d8506da1c31926beef".
For example, in the file getDogs.js, using getDogSlice:
// pages/api/getDogs.js const dogCollectionId = process.env.DOG_COLLECTION_ID; async function getDogSlice(serials, idOnly = false) { const nfts = await getCollectionNFTs({ collectionId: dogCollectionId, serials, idOnly }); return nfts; } // ... }
Setting Up Environment Variables on Netlify
In order for your Sample App to work properly once deployed, you need to setup the Environment Variables on the server.
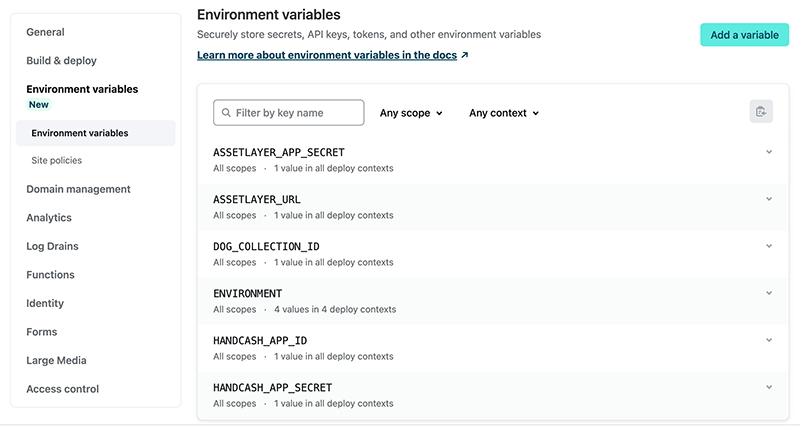
Read more about environment variables here.